When exploring credit card options, understanding APR, or Annual Percentage Rate, is crucial. The APR represents the yearly cost of borrowing money on a credit card, including interest and any associated fees. Learning how to evaluate and compare APRs can help you make informed financial decisions and select the best credit card for your needs.
By understanding how APRs impact your payments, you can avoid unnecessary costs and confidently manage your credit card expenses.
APR Explained to Help You Choose the Best Credit Card
APR stands for Annual Percentage Rate. APR represents the yearly cost of borrowing money through your credit card. It includes the interest rate as well as any additional fees charged by the card issuer. Essentially, APR tells you how much it will cost to carry a balance on your credit card from month to month.
Let’s understand the APR with practical example,
Imagine you have a credit card with an APR of 20%. This means that if you borrow $1,000 using your credit card and you don’t pay it back right away, you’ll owe an extra 20% of that amount in one year. So, after one year, you’d owe $1,200 ($1,000 + 20% of $1,000).
But here’s the tricky part: APR is calculated on an annual basis, but credit card companies typically charge interest every month. So, if you don’t pay off your balance in full each month, you’ll end up owing even more because interest keeps adding up on the remaining balance.
Let’s say you only pay the minimum amount due each month, and your credit card company charges interest monthly. If your balance is $1,000, and your APR is 20%, then you’d owe about $16.67 in interest for the first month ($1,000 * 20% / 12 months). This interest gets added to your balance, so now you owe $1,016.67. And the cycle continues.
So, the APR is important because it gives you an idea of how much extra you’ll pay if you don’t pay off your credit card balance in full each month. It’s crucial to understand your card’s APR to make smart decisions about borrowing money with your credit card.
Why APR Matters for Your Credit Card Decisions
- Cost of Borrowing: A lower APR means paying less interest if you carry a balance. Choosing a card with a low APR can save you money in the long run if you expect to carry a balance.
- Introductory APR Offers: Many cards offer introductory periods with 0% APR on purchases or balance transfers. These are helpful for making large purchases or consolidating debt without accruing interest for a set time.
- Comparison Shopping: Considering the APR is crucial when comparing cards. Even if a card offers appealing rewards, a high APR could negate those benefits if you carry a balance.
- Financial Planning: Understanding APR enables you to make informed financial decisions. Prioritizing a card with a lower ongoing APR can offer more flexibility, especially if you anticipate occasionally carrying a balance.
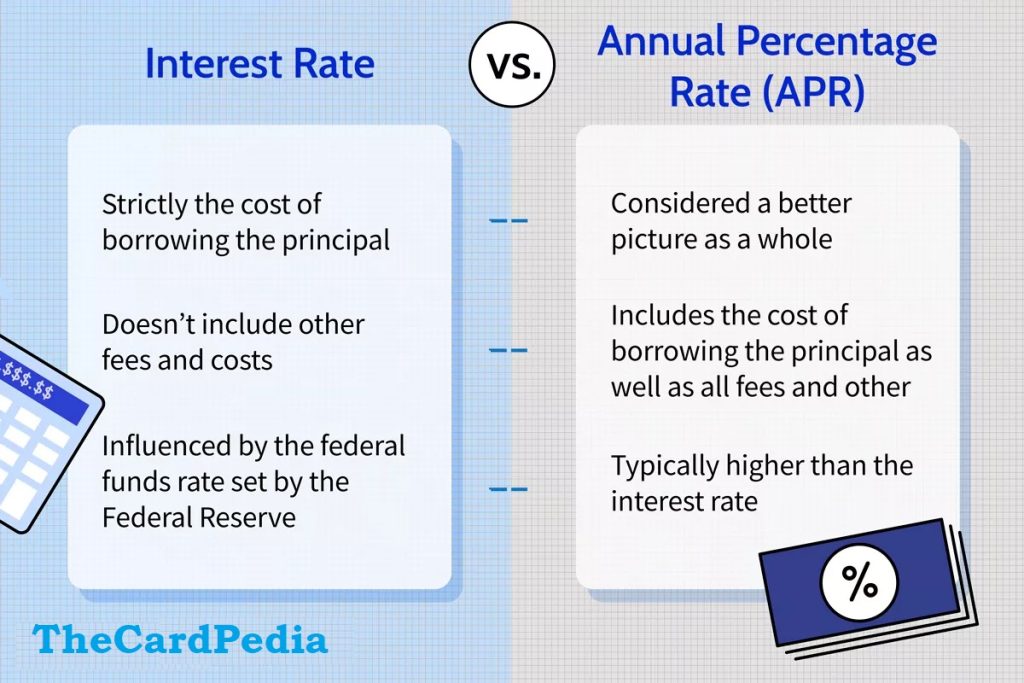
Interest Rate vs. APR: What’s the Difference?
Interest rate and APR are terms commonly used when discussing borrowing money, but they have distinct meanings. Let’s explore the key differences between the two while Choosing the Right Credit Card.
Types of Credit Card APRs
Credit cards come with different types of APRs (Annual Percentage Rates) that determine the interest you’ll pay on various transactions. Understanding these APRs can help you manage your finances better and avoid unnecessary charges.
- Purchase APR: This is the interest rate charged on new purchases if you don’t pay off your balance in full each month by the due date. It applies to any new purchases you make with your credit card.
- Balance Transfer APR: When you transfer a balance from one credit card to another, you’ll be charged this interest rate on the transferred amount. It’s important to check the terms and conditions of balance transfers, including any associated fees.
- Introductory APR: Some credit cards offer a special introductory APR, usually lower or even 0%, for a limited time after you open an account. This can apply to purchases, balance transfers, or both. However, once the introductory period ends, the standard APR will apply to any remaining balance.
- Cash Advance APR: This is the interest rate applied to cash withdrawals made from your credit card’s line of credit. Cash advances often come with higher APRs compared to purchases and balance transfers, along with additional fees and no grace period, making them expensive to use.
- Penalty APR: If you miss a payment or pay late, the credit card issuer may impose a penalty APR, which is usually higher than the standard rate. This penalty APR can apply indefinitely and may nullify any introductory APR offers. Late payments can also negatively affect your credit score.
Understanding these different APRs can help you make informed decisions about using your credit card and avoid unnecessary fees and charges
🚀 Check: How to Improve Your Credit Score for Better Loan Options
Comparing High APR and Low APR Credit Cards: Making the Right Choice
When choosing between high APR and low APR credit cards, it’s essential to understand the implications of each. Let’s explore the differences between these types of Credit cards with specific examples to help you make an informed decision:
High APR Credit Cards
- Example: Capital One Quicksilver Cash Rewards Credit Card (APR: 19.24% – 29.99% Variable)
- Pros: Often come with lucrative rewards programs, such as cashback or travel points, and may offer extended 0% APR introductory periods for purchases or balance transfers.
- Cons: Carry significantly higher interest rates compared to low APR cards. If you don’t pay your balance in full each month, the interest charges can quickly outweigh any rewards earned.
Low APR Credit Cards
- Example: Discover it® Cash Back (APR: 15.99% – 24.99% Variable)
- Pros: Offer lower interest rates, minimizing the cost of carrying a balance. This can be especially beneficial for individuals who occasionally need to carry a balance due to unexpected expenses.
- Cons: Typically have fewer or less valuable rewards programs compared to high APR cards. They may also have annual fees associated with them.
🌍 Read more: Chase Sapphire Reserve Credit Card Review 2025: Is It Worth the Annual Fee?
Choosing the Right Credit Card
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your financial habits and priorities. Here’s a breakdown to help you decide:
- Pay your balance in full each month: If you consistently pay your balance in full each month, a high APR card with attractive rewards can be beneficial. You can earn valuable rewards without incurring interest charges.
- Carry a balance occasionally: If you occasionally need to carry a balance, a low APR card is a better option. The lower interest rate will save you money on interest charges in the long run, even if the rewards program is less generous.
- Struggle with managing credit card debt: If you find it challenging to manage credit card debt, it might be best to avoid high APR cards altogether. Consider using a debit card or a secured credit card to build your credit history responsibly.
Remember, consider your spending patterns, repayment capabilities, and financial goals when deciding between high APR and low APR credit cards. By choosing the Popular Credit Card that aligns with your needs, you can maximize your financial well-being and make the most of your credit card experience.
At TheCardPedia.com, we’re your trusted guide to mastering credit cards. Explore expert insights, trends, and tips to make savvy financial choices. Start your journey to financial empowerment now!
[…] Percentage Rate (APR): The interest rate charged on unpaid […]